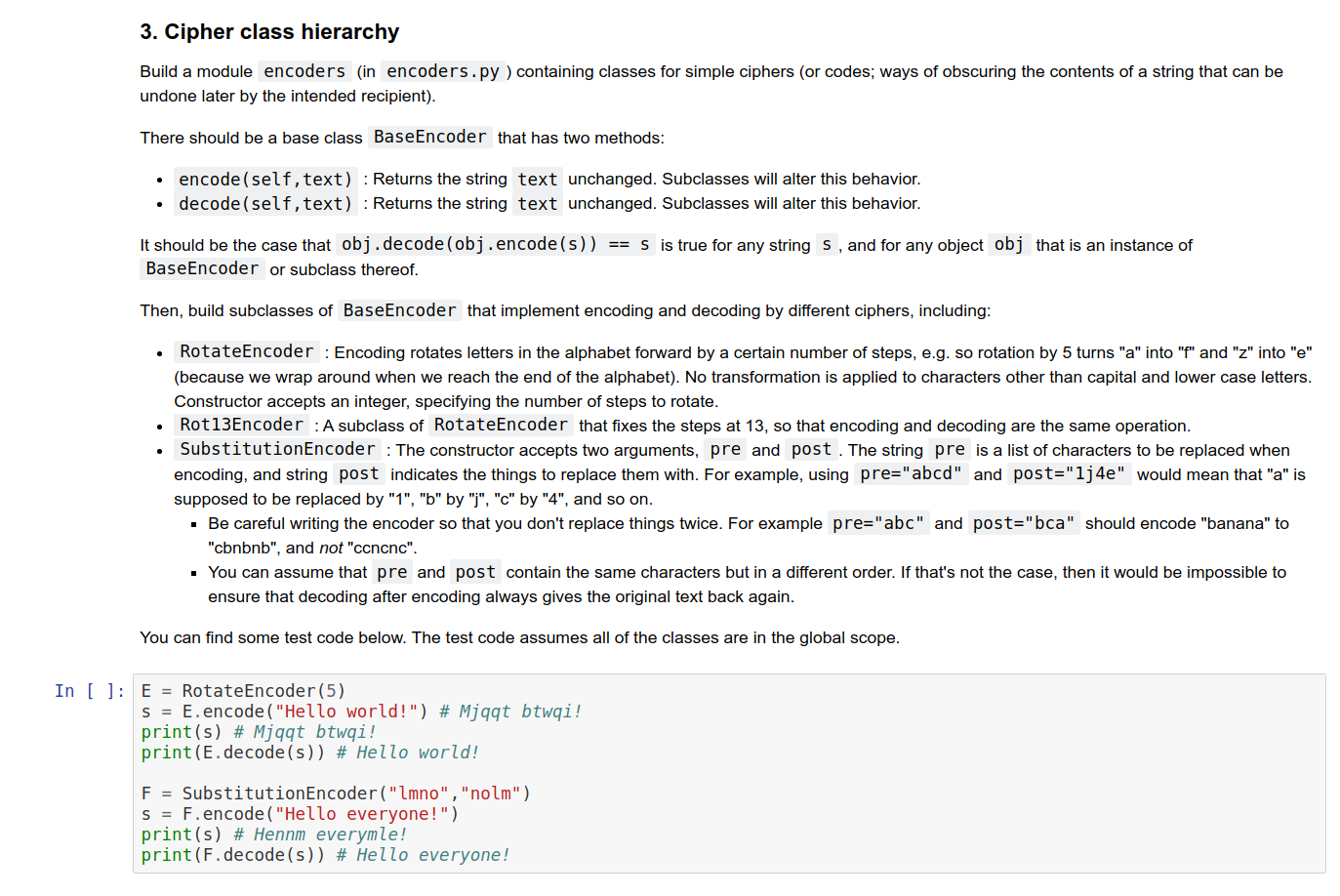
Lecture 7
Notebooks
MCS 275 Spring 2022
Emily Dumas
Lecture 7: Notebooks
Course bulletins:- Project 1 deadline 6pm central on Fri Feb 4.
- Project 1 autograder opens on Monday.
Project 1
- Major focus is reading existing code.
- Uses object-oriented programming.
- You must add a few subclasses of an existing class.
Project 1 files
| bacteria.py | The only file you submit; add subclasses as requested |
|---|---|
| environment.py | Read, don't modify |
| plane.py | Read if needed, don't modify |
| textsimulation.py | Use/modify for testing |
Project 1
Now, a demo of a solution to the project in the REPL and using textsimulation.py.
Python interfaces
- REPL — One command at a time. Result is printed.
- Script mode — Runs an entire file. Nothing printed unless explicitly requested (e.g.
print(...)).
Python interfaces
- REPL — One command at a time. Result is printed.
- Notebook — Make groups of commands (cells) to run when ready. Last result in a cell is printed.
- Script mode — Runs an entire file. Nothing printed unless explicitly requested (e.g.
print(...)).
What notebooks look like
MCS 275 uses notebooks for homework, worksheets, and project descriptions, so you've seen these before. But you usually see a version converted to HTML.
What notebooks look like

MCS 275 uses notebooks for homework, worksheets, and project descriptions, so you've seen these before. But you usually see a version converted to HTML.
What notebooks look like

MCS 275 uses notebooks for homework, worksheets, and project descriptions, so you've seen these before. But you usually see a version converted to HTML.
How to use notebooks
Several options:- Google Colab — Web tool to create, edit, run notebooks. Need a Google account. Can save or download notebooks.
- Other online provider, e.g. Kaggle, CoCalc
- Jupyter — Software you install locally to create, edit, run notebooks. Browser shows the UI.
- VS Code — Has an extension for handling notebook files.
Jupyter install instructions
Most users can install Jupyter using pip:
python -m pip install notebookThen run the interface with:
python -m notebookOf course, you need to replace python with your interpreter name.
Using Colab / Jupyter
A few of the many keyboard shortcuts:
- shift-enter — run the current cell
- escape — switch from cell editing to navigation
- a — in nav mode, add a new cell ABOVE this one
- b — in nav mode, add a new cell BELOW this one
- dd — in Jupyter, in nav mode, delete current cell (colab has a delete button, and a different shortcut)
- m — in Jupyter, in nav mode, make current cell a Markdown (text) cell
Markdown
Text cells (Colab) or markdown cells (Jupyter) contain formatted text. When editing, formatting is specified with a language called Markdown.
# Heading level 1
## Heading level 2
### Heading level 3
* Bullet list item
* Another bullet list item
1. Numbered list item
1. Another numbered list item
Links: [text to display](https://example.com)
References
- Google Colab offers notebook creation, editing, execution (can use netid@uic.edu google account).
- Some other online services allowing free use of Python notebooks: Kaggle, CoCalc
- See Lutz, Chapter 18 for more about function arguments (including variadic functions).
- A Markdown guide from GitHub.
Revision history
- 2022-01-26 Initial publication
- 2022-01-26 Remove variadic stuff we didn't cover (coming next time)